High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI)
Thursday, August 28, 2008
Jitter and Eye Measurements: Ideal Recovery Clock
signal jitter specifications are specified relative to an Ideal Recovery
Clock defined below. The Data jitter is not specified numerically, but
instead, an High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) device or cable
shall adhere to the appropriate eye diagram(s) when the Transition
Minimized Differential Signaling (TMDS) data signals are measured using an
Ideal Recovery Clock as a trigger source.
The Transition Minimized Differential Signaling (TMDS) Clock signal may
contain low-frequency jitter components, which can be tracked by a Sink's
clock recovery circuitry, and high-frequency components, which are not
typically tracked. The purpose of the Ideal Recovery Clock is to give an
accurate representation of link performance when used as a trigger for eye
diagram and clock jitter specifications. The eye mask specifies the
relationship of clock jitter to data jitter only indirectly.
For the purposes of jitter and eye diagram specification, the Ideal
Recovery Clock is defined relative to the Transition Minimized Differential
Signaling (TMDS) clock signal. The Ideal Recovery Clock shall be equivalent
to the signal that would be derived by a perfect PLL (Ideal Clock Recovery
Unit) with a jitter transfer function shown in 'Jitter Transfer Function'
Equation, when the Transition Minimized Differential Signaling (TMDS) clock
signal were input into that PLL. This jitter transfer function has the
behavior of a low pass filter with 20dB/decade roll-off and with a –3dB
point of 4MHz.
(See attached file: Jitter Transfer Function of ideal CRU.jpg)
For the purposes of compliance testing, a Clock Recovery Unit is used to
generate a Recovered Clock, which is meant to approximate the Ideal
Recovery Clock. This Recovered Clock is used for measurement of the jitter
and eye diagram.
Wednesday, August 20, 2008
Transition Minimized Differential Signaling Overview (TMDS Overview)
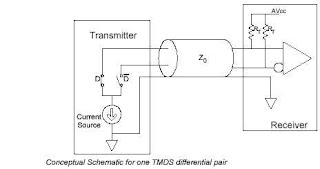
Signaling) differential pair is shown in 'Conceptual Schematic for one TMDS
differential pair' Figure. (See attached file: Conceptual schematic for one
TMDS differential pair.jpg)TMDS technology (transition minimized
differential signaling technology) uses current drive to develop the low
voltage differential signal at the Sink side of the DC-coupled transmission
line. The link reference voltage AVcc sets the high voltage level of the
differential signal, while the low voltage level is determined by the
current source of the HDMI Source and the termination resistance at the
Sink. The termination resistance (RT) and the characteristic impedance of
the cable (Z0) must be matched.
A single-ended differential signal, representing either the positive or
negative terminal of a differential pair, is illustrated in 'Single-ended
differential signal' Figure. The nominal high-level voltage of the signal
is AVcc and the nominal low-level voltage of the signal is (AVcc - Vswing).
Since the swing is differential on the pair, the net signal on the pair has
a swing twice that of the single-ended signal, or 2 Vswing. The
differential signal, as shown in 'Differential signal' Figure, (See
attached file: Differential signal.jpg) swings between positive Vswing and
negative Vswing.
The signal test points for a TMDS link (Transition Minimized Differential
Signaling Link) are shown in 'TMDS Link Test Points' Figure. (See attached
file: TMDS Link Test Points.jpg) TP1 is used for testing of HDMI Sources
and Transmitter components. TP2 is used for testing of HDMI Sinks and
Receiver components. TP1 and TP2 together are also used for testing of
cables.
Tuesday, August 19, 2008
High Definition Multimedia Interface - HDMI Physical Layer Electrical Specification
rate of the link while others are based on absolute values. For scalable
timing parameters based on the TMDS clock rate (Transition Minimized
Differential Signaling Clock Rate), the time period of the clock is denoted
as 'TMDS character time', or, 'Transition Minimized Differential Signaling
Character Rate', or Tcharacter. One tenth of the character time is called
the bit time, or Tbit. The bit time is also referred to as one Unit
Interval in the jitter and eye diagram specifications.
Schematic diagrams contained in this chapter are for illustration only and
do not represent the only feasible implementation.
Transition Minimized Differential Signaling Overview (TMDS Overview)
The conceptual schematic of one TMDS (Transition Minimized Differential
Signaling) differential pair is shown in 'Conceptual Schematic for one TMDS
(Transition Minimized Differential Signaling) differential pair' Figure.
(See attached file: Conceptual schematic for one TMDS differential
pair.jpg) TMDS technology (transition minimized differential signaling
technology) uses current drive to develop the low voltage differential
signal at the Sink side of the DC-coupled transmission line. The link
reference voltage AVcc sets the high voltage level of the differential
signal, while the low voltage level is determined by the current source of
the HDMI Source and the termination resistance at the Sink. The termination
resistance (RT) and the characteristic impedance of the cable (Z0) must be
matched.
A single-ended differential signal, representing either the positive or
negative terminal of a differential pair, is illustrated in 'Single-ended
differential signal' Figure. (See attached file: Single-ended differential
signal.jpg) The nominal high-level voltage of the signal is AVcc and the
nominal low-level voltage of the signal is (AVcc - Vswing). Since the swing
is differential on the pair, the net signal on the pair has a swing twice
that of the single-ended signal, or 2 Vswing. The differential signal, as
shown in 'Differential signal' Figure, (See attached file: Differential
signal.jpg) swings between positive Vswing and negative Vswing.
The signal test points for a TMDS link (Transition Minimized Differential
Signaling Link) are shown in 'TMDS Link Test Points' Figure. (See attached
file: TMDS Link Test Points.jpg) TP1 is used for testing of HDMI Sources
and Transmitter components. TP2 is used for testing of HDMI Sinks and
Receiver components. TP1 and TP2 together are also used for testing of
cables.